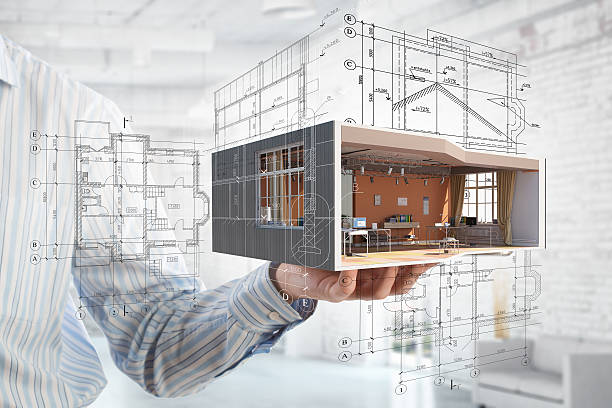
Architectural Design: The Ultimate Guide to Creative Excellence 2025
Architectural design is more than just constructing buildings; it is an intricate blend of art, science, and functionality. The term architectural design refers to the planning, conceptualization, and execution of physical structures that reflect both utility and aesthetics. It is a discipline that requires not only technical expertise but also a deep understanding of cultural and environmental contexts.
What is Architectural Design?
At its core, architectural design involves creating a blueprint that balances form and function. It is about shaping spaces to meet human needs while considering structural integrity, sustainability, and visual appeal. From skyscrapers to homes, architectural design plays a pivotal role in defining how we live, work, and interact with our environment.
Key Principles of Architectural Design
1. Functionality
A primary goal of architectural design is to ensure the structure serves its intended purpose efficiently. Whether it’s a commercial building or a residential home, the layout must cater to the user’s needs. For instance, open spaces in modern office designs promote collaboration, while private zones enhance focus.
2. Aesthetic Appeal
Architectural design is an art form that marries beauty with functionality. A building’s visual impact is as crucial as its utility. The use of materials, textures, and colors all contribute to the aesthetic charm of the design.
3. Sustainability
Modern architectural design emphasizes eco-friendly solutions. Sustainable practices, such as using renewable materials and energy-efficient systems, are now integral to the design process.
4. Contextual Integration
Every architectural design should respect its surroundings. Whether it blends seamlessly with nature or contrasts boldly against urban landscapes, the design must reflect its environment and cultural heritage.
Types of Architectural Design
1. Residential Design
Focused on homes and living spaces, this type of architectural design prioritizes comfort, safety, and personalization. From luxurious villas to compact apartments, residential designs cater to diverse lifestyles.
2. Commercial Design
This includes office buildings, malls, and retail spaces. Commercial architectural design revolves around maximizing utility, enhancing customer experiences, and incorporating branding elements.
3. Industrial Design
Industrial architectural design deals with factories, warehouses, and other facilities. It emphasizes efficiency, durability, and compliance with safety standards.
4. Landscape Design
This aspect of architectural design focuses on outdoor spaces, such as gardens, parks, and public plazas. The aim is to create harmonious environments that encourage relaxation and community interaction.
The Role of Technology in Architectural Design
Technology has revolutionized architectural design, enabling architects to explore innovative solutions and streamline workflows. Tools like Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Building Information Modeling (BIM) allow for precise planning, visualization, and project management. Virtual reality further enhances client presentations by providing immersive previews of designs.
Challenges in Architectural Design
1. Balancing Cost and Quality
Architects often face the challenge of delivering high-quality designs within budget constraints. Cost-effective material choices and innovative solutions are essential to address this issue.
2. Adhering to Regulations
Strict building codes and zoning laws can limit creativity in architectural design. Architects must navigate these restrictions without compromising their vision.
3. Addressing Climate Concerns
With the growing emphasis on sustainability, architects are tasked with incorporating green technologies while maintaining practicality and affordability.
The Future of Architectural Design
The evolution of architectural design is influenced by trends such as smart buildings, modular construction, and biophilic designs. As technology advances and environmental concerns grow, the future promises more innovative, sustainable, and adaptive architectural solutions.
Architectural Design in Different Cultures
The diversity of architectural design reflects the uniqueness of global cultures. Traditional Japanese architecture, with its minimalism and harmony with nature, contrasts starkly with the intricate ornamentation of Baroque design found in Europe. Each culture has its distinct approach to materials, shapes, and construction methods, showcasing the universal yet diverse nature of this field.
Examples of Cultural Influence
- Middle Eastern Design: Known for its geometric patterns and intricate details, this style emphasizes grandeur and symmetry.
- Scandinavian Architecture: Focused on simplicity and functionality, it embodies clean lines and natural materials.
- Indigenous Architecture: From adobe homes in the Americas to bamboo structures in Asia, indigenous designs reflect adaptability to local climates and resources.
The Impact of Architectural Design on Society
Architectural design influences not only the physical landscape but also the social and emotional well-being of individuals. Well-designed urban spaces encourage community interactions, while poorly planned environments can lead to congestion and stress.
Urban Design and Community Development
Modern cities prioritize mixed-use developments, green spaces, and walkability. These features promote a sense of community and improve the overall quality of life. Architectural design is at the heart of creating vibrant, livable cities.
Educational Paths in Architectural Design
Pursuing a career in architectural design requires a strong educational foundation. Most architects hold degrees in architecture or related fields, where they learn principles of design, engineering, and sustainability.
Skills for Aspiring Architects
- Creative Thinking: Generating innovative solutions for complex problems.
- Technical Proficiency: Mastery of tools like AutoCAD, BIM, and 3D modeling software.
- Communication Skills: Articulating design ideas effectively to clients and collaborators.
Sustainability in Architectural Design
The rise of green architecture has transformed the field of design. Architects now integrate sustainable practices to minimize environmental impact. This includes using renewable materials, incorporating energy-efficient systems, and designing for natural ventilation.
Examples of Sustainable Practices
- Green Roofs: Enhancing insulation and promoting biodiversity.
- Solar Panels: Reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
- Passive Design Techniques: Leveraging natural light and airflow for temperature regulation.
Renowned Architects and Their Contributions
Throughout history, visionary architects have redefined the boundaries of architectural design. Their works continue to inspire and shape the profession.
Iconic Figures in Architectural History
- Frank Lloyd Wright: Known for his organic architecture that harmonizes with nature.
- Zaha Hadid: A pioneer in futuristic, fluid designs that defy convention.
- Le Corbusier: An advocate for functionalism and modern urban planning.
Why Architectural Design Matters
Architectural design is more than a technical process; it is a reflection of human creativity and ingenuity. From enhancing daily living to addressing global challenges like climate change, it plays a vital role in shaping a better future.
Frequently Asked Questions About Architectural Design
1. What is architectural design, and why is it important?
Architectural design involves planning and creating functional and aesthetic structures. It is crucial because it shapes our living and working environments, ensuring comfort, sustainability, and harmony with the surroundings.
2. How does architectural design differ from engineering?
While architectural design focuses on the aesthetics, functionality, and usability of a space, engineering emphasizes the technical aspects like structural integrity and safety. Both work together to create effective designs.
3. What are the key principles of good architectural design?
Good architectural design balances functionality, aesthetics, sustainability, and contextual relevance. It prioritizes user experience while respecting environmental and cultural factors.
4. How has technology influenced architectural design?
Technology, such as CAD and BIM software, has revolutionized architectural design by enhancing precision, creativity, and collaboration. Virtual and augmented reality also allow for immersive client presentations.
5. How can architectural design incorporate sustainability?
Sustainable architectural design includes using eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient systems, and passive design techniques like natural ventilation and lighting.
6. What role does cultural context play in architectural design?
Cultural context greatly influences architectural design by dictating styles, materials, and construction techniques that resonate with local traditions and values.
7. Can architectural design impact mental health?
Yes, well-designed spaces can positively affect mental health by reducing stress, enhancing comfort, and promoting social interactions. Poorly designed environments, on the other hand, may lead to discomfort and stress.